Heat is a type of energy that we can feel. The hotter something is, the more heat energy it gives out. Heat energy always tries to spread from a hotter to colder things. So, when you touch a hot object, heat energy flows out of the object into you, warming you up.
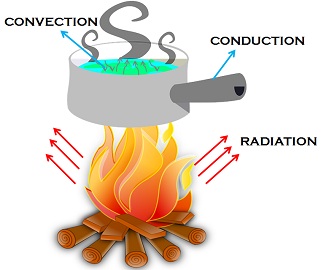
Conduction
Heat energy spreads out through solid objects by conduction. Metal objects are very good conductors of heat, so heat energy pass through them quickly and easily.
Convection
When gases and liquids get hot, heat energy spreads out through them by convection. Hot air or water rises, and cold air or water sinks to take its place.
Radiation
Heat escapes from the surface of hot objects by invisible rays that travel through air and space. This is how we feel the heat from the Sun. hotter objects give out more radiation than cooler ones.
Temperature
Temperature is the measure of how hot or cold things are. It is recorded in degrees Celsius (ºC) or degrees Fahrenheit (ºF).
15 millionºC (27 millionºF)
The temperature at the centre of the Sun.
1760ºC (3,200ºF)
The temperature at which sand melts and turns into glass.
232ºC (450ºF)
The temperature at which dry wood catches fire.
100ºC (212ºF)
The boiling point of water.
56.7ºC (134ºF)
The hottest temperature recorded on Earth at Death Valley, California, USA, on 10 July 1913.
37ºC (98.6ºF)
The average temperature of the human body.
2ºC (35.6ºF)
The temperature of the air when rain turns to snow.
0ºC (32ºF)
The freezing point of water.
89.2ºC (-128.5ºF)
The coldest temperature recorded on Earth at Vostock Station, Antarctica, in 1983.
-272ºC (-458ºF)
The temperature of the Boomerang Nebula, a cloud of dust and gas that is the coldest place in the Universe.
Picture Credit : Google




