This front view of the skeleton shows the body’s deepest layer of skeletal muscles. Skeletal muscles in the back and neck work to keep the body upright, while those in the arms and legs are used for walking, running, and all kinds of other physical activities.
Sternothyroid
This strap-like muscle at the front of the neck the larynx down. It is a part of a group of muscles called the infrahyoid muscles. There are four such muscles that are grouped into superficial and deep layers.
Pectoralis minor
This muscle helps to stabilize the shoulder blade when the arm moves. It is one of the anterior axioappendicular (thoracoappendicular) muscles, together with the pectoralis major, subclavius and serratus anterior.
Together with other muscles of the region it produces various movements of the scapula and can be used as an accessory muscle of respiration.
Brachialis
The brachialis helps to bend the elbow. It is fusiform in shape and located in the anterior (flexor) compartment of the arm, deep to the biceps brachii. The brachialis is a broad muscle, with its broadest part located in the middle rather than at either of its extremities.
Intercostal muscles
These muscles between the ribs help with breathing by raising the ribs up and out. The muscles are broken down into three layers, and are primarily used to assist with the breathing process. The three layers are: external intercostal muscles, internal intercostal muscles, and the innermost intercostal muscles.
Posterior rectus sheath
This tissue is formed by the tendons of abdominal muscle. It is an extension of the tendons of the external abdominal oblique, internal abdominal oblique, and transversus abdominis muscles.
Transversus abdominis
This muscle helps to stabilize the pelvis and lower back when moving. Along with the external abdominal oblique and the internal abdominal oblique, it comprises the lateral abdominal muscles. Combined with the two anterior abdominal muscles (rectus abdominis and pyramidalis), these muscles make up the anterolateral abdominal wall.
Flexor digitorum profundus
This muscle helps to bend the fingers. Flexor digitorum profundus is a fusiform muscle located deep within the anterior (flexor) compartment of the forearm. Along with the flexor pollicis longus and pronator quadratus muscles, it comprises the deep flexor compartment of the forearm.
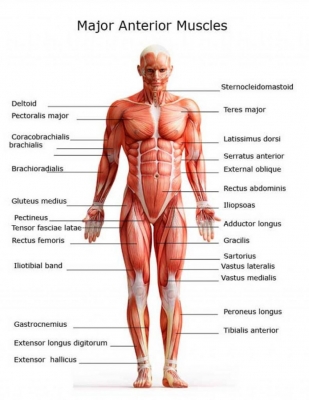
Gluteus medius
This muscle moves the thigh outwards. Together with the gluteus maximus, gluteus minimus and tensor fasciae latae muscles, it belongs to the muscles of the gluteal region.
Pectineus
This muscle helps to lift the thigh. Fascial compartments of the thigh muscles are specific in that each of them is innervated by a particular nerve. Due to having dual innervation, pectineus is one of a few muscles classified into two compartments at the same time; anterior and medial. The others being adductor longus and adductor magnus.
Adductor compartment of thigh
These muscles bring the thighs together. The adductor magnus is the largest muscle in the medial compartment. It lies posteriorly to the other muscles.
Functionally, the muscle can be divided into two parts; the adductor part, and the hamstring part.
Vastus intermedius
This is one of the four parts of the strong quadriceps muscle at the front of the thigh. Vastus Intermedius is located centrally, underneath Rectus femoris in the anterior compartment of the thigh and on each side of it: Vastus medialis and Vastus Lateralis respectively. It is one of the four muscles that form the quadriceps femoris muscle. Tensor of Vastus Intermedius is a new muscle that is part of the Quadriceps.
Patella (kneecap)
The patella is the kneecap bone. It lies within the quadriceps tendon. This large tendon from the powerful thigh muscles (quadriceps) wraps round the patella and is attached to the top of the lower leg bone (tibia). The quadriceps muscles straighten the knee.
Extensor digitorum longus
This long muscle lifts up the foot and the toes. Besides EDL muscle, this compartment also contains the tibialis anterior, extensor hallucis longus and fibularis (peroneus) tertius muscles.
Picture Credit : Google

