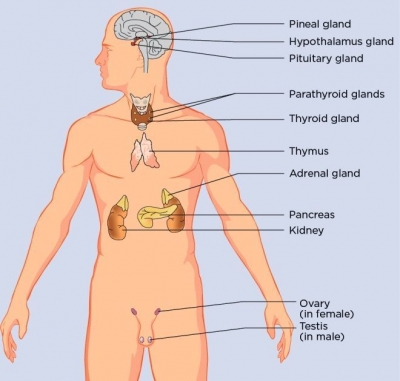
Hormone factory
The main hormone-producing glands are in the brain, neck, abdomen, and groin. Other organs, such as the stomach, liver, and heart, release hormones, too. Hormones are released only when the gland receives the correct trigger – a change in blood, a nerve signal, or an instruction from another hormone.
Thymus
The thymus secretes hormones to boost the production of disease-fighting white blood cells. It is only active during childhood and early teenage years, and shrinks to be almost invisible in adults.
Pineal gland
The pineal body is located below the corpus callosum, in the middle of the brain. This gland makes melatonin, which affects sleep.
Hypothalamus
The hypothalamus is located at the base of the brain, near the optic chiasm ???where the optic nerves behind each eye cross and meet. This parts o the brain links the nervous and endocrine systems.
Pituitary gland
The pituitary gland is located below the brain. Usually no larger than a pea, the gland controls many functions of the other endocrine glands. Hormones that control other glands are produced here.
Thyroid gland
This gland releases thyroxine, which controls the body’s metabolic rate – the speed at which cells use up the oxygen that fuels them.
Parathyroid glands
These four small glands regulate levels of calcium, which is vital for healthy teeth and bones.
Heart
The heart releases hormones that control blood pressure.
Stomach
The walls of the stomach secrete gastrin, which triggers the release of digestive juices when we eat.
Adrenal glands
These glands produce hormones that control salt levels, as well as adernaline, which prepares the body to respond to danger. The adrenal glands make and release corticosteroid hormones and epinephrine that maintain blood pressure and regulate metabolism.
Pancreas
The pancreas is located across the back of the abdomen, behind the stomach. The pancreas plays a role in digestion, as well as hormone production. The pancreas makes insulin and glucagon, which control glucose levels in the blood.
Small intestine
This organ releases hormones that help with digestion.
Ovaries
A woman’s ovaries are located on both sides of the uterus, below the opening of the fallopian tubes (tubes that extend from the uterus to the ovaries). Ovaries produce the sex hormones pestrogen and progesterone, which control a woman’s reproductive cycle.
Testes
Also called testicles, these release the male sex hormone testosterone, which triggers the production of sperm.
Picture Credit : Google

