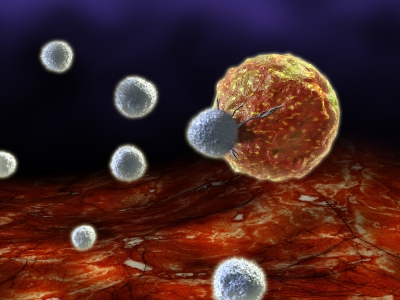
Even if some pathogens manage to get past the body’s first line of defence, they are unlikely to beat the many millions of white blood cells.
White blood cells
The immune system is run by white blood cells, which move through the bloodstream and other bodily fluids looking for bacteria and viruses to kill. Most white blood cells are made inside bone marrow tissue, and more are produced when germs are present.
- Macrophage: This type of white blood cell kills bacteria and other germs by engulfing them and eating them.
- Lymphocyte: This type learns to attack only one type or germ by filling it with poison or releasing antibodies.
- Neutrophil: This is the most common type of white blood cell. Neutrophils help to fight bacteria and fungi.
Appetite for destruction
Macrophages hunt invading bacteria by following the chemical trails they leave behind. If these hungry white blood cells track down an invader, they surround and swallow it. Each macrophage eats about 200 bacteria before it dies.
- Plan of attack: A macrophage identifies bacteria as enemies and prepares to attack.
- Killer chemicals: The bacteria are captured, surrounded, and digested by powerful chemicals.
- Hungry hunter: The macrophage expels harmless waste and carries on hunting for invaders.
Fighting inflammation
When the skin is broken by a cut, the body’s defence team responds at once. Damaged tissues release chemicals to attract white blood cells, ready to destroy pathogens. Blood vessels allow blood to leak out, so platelets and white blood cells can reach the site of the wound.
- Injury: The skin is pierced. Blood vessels respond by getting wider to increase blood flow to the site. Exposed tissue leaves germs and dirt free to enter.
- Blood clot: Platelets thicken the blood to create a clot that seals the wound. White blood cells arrive, looking for pathogens to destroy.
- Germ eaters: The white blood cells consume the pathogens. The tissue and skin can now begin to repair itself.
Picture Credit : Google

