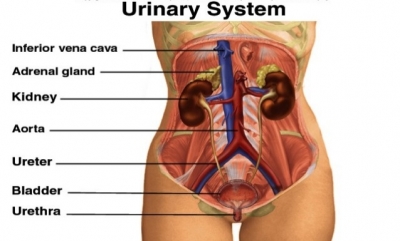
The urinary system consists of two kidneys, two ureters, a bladder, and a urethra. The kidney’s process the blood’s waste into urine, which passes through the ureters to the bladder. When the bladder is full, pressure sensors send signals to the brain. Humans are not born with the ability to control the urge to urinate. Children start to learn bladder control from about the age of two.
Female urinary system
Left kidney
This is one of two bean-shaped organs that filter blood to make urine.
Renal vein
The two renal veins carry filtered blood to the heart, from where it can be pumped around the body again. The right renal vein receives tributaries exclusively from the kidney, while the left renal vein receives several tributaries from other organs, including the left gonadal (ovarian/testicular) vein, left inferior phrenic vein and left adrenal veins.
Renal artery
The renal arteries bring unfiltered blood to the kidneys. The renal artery enters through the hilum, which is located where the kidney curves inward in a concave shape. Under normal circumstances, once the renal artery enters through the hilum, it splits into two main branches, which each then split into numerous smaller arteries, which deliver blood to different areas of the kidneys, known as nephrons. Once the blood has been processed here, it is sent back through the renal vein to the inferior vena cava and to the right side section of the heart.
Right kidney
This organ sits slightly lower than the left kidney, beneath the liver.
Left ureter
A one-way flow of urine is carried by the ureters from the kidneys to the bladder. The left ureter, however, travels laterally to the inferior mesenteric vessels and is subsequently crossed by its branches.
Inferior vena cava
The inferior vena cava (IVC) is the largest vein of the human body. It is located at the posterior abdominal wall on the right side of the aorta. Oxygen-poor blood is carried towards the heart in this large vein.
Abdominal aorta
The abdominal aorta is the final section of the aorta, the largest artery in the body. It is a continuation of the thoracic aorta. It begins at the diaphragm, and runs down to the point where it ends (by splitting in two to form the common iliac arteries). This main artery carries oxygen-rich blood from the heart.
Right ureter
As the right ureter travels towards the bladder, it travels posterior to the duodenum and further down it is crossed by branches of the superior mesenteric vessels.
Bladder
The urinary bladder is a muscular sac in the pelvis, just above and behind the pubic bone. When empty, the bladder is about the size and shape of a pear. The bladder is a storage bag that holds urine from the kidneys until it is ready to be released.
Urethra
The urethra carries urine from the bladder out of the body. In men, the urethra is about 8 inches (20 centimeters) long, ending at the tip of the penis. In women, the urethra is about 1½ inches (4 centimeters) long, ending at the vulva (the area of the external female genital organs).
Male urinary system
A male’s urinary system is the same as females, except that the urethra is longer and passes along the penis.
Picture Credit : Google




