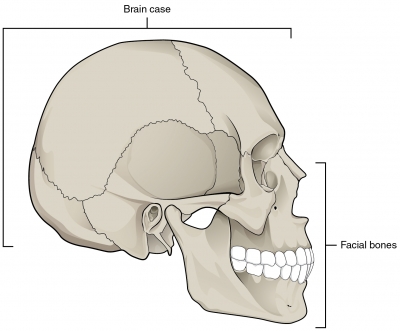
Cranium
This is the domes part of the skull. The cranium (skull) is the skeletal structure of the head that supports the face and protects the brain.
Nasal bone
These bones form the bridge of the nose. Their superior borders and main bodies form the bridge of the nose while the inferior borders connect with the nasal cartilage to form the superior margin of the nasal aperture.
Sinuses
The sinuses make up a network of air-filled holes inside the skull. These spaces make the skull lighter, and act as soundboxes to change the tone of your voice when you speak.
Frontal sinuses
These cavities, above the eyebrow ridge, form after birth and reach full size by the teenage years.
Lower jaw
Also called the mandible, this is the largest bone in the skull, and the only one that can move. Movement of the lower jaw opens and closes the mouth and also allows for the chewing of food. The lower set of teeth in the mouth is rooted in the lower jaw.
Hyoid bone
The hyoid bone is a ‘U’ shaped structure located in the anterior neck. It lies at the base of the mandible (approximately C3), where it acts as a site of attachment for the anterior neck muscles. This bone forms the base for the tongue.
Frontal bone
The forehead is formed from this bone. The frontal bone creates the smooth curvature of the forehead and protects the frontal lobe of the brain, especially the ethmoid bone’s horizontal plate known as the cribriform plate which allows the olfactory nerve bundles to pass through its perforated surface and bring the ceiling of the nasal cavity its sense of smell.
Orbit
The orbit can be thought of as a pyramidal structure, with the apex pointing posteriorly and the base situated anteriorly. Seven bones form the orbit or eye socket.
Foramen
Tiny openings in the skull allow nerves and blood vessels to pass through. The word foramen comes from the Latin word meaning “hole.” Essentially, all of the foramen (singular), or the foramina (plural of foramen), in the skull are holes. They are passageways through the bones of the skull that allow different structures of the nervous and circulatory system to enter and exit the skull.
Picture Credit : Google




