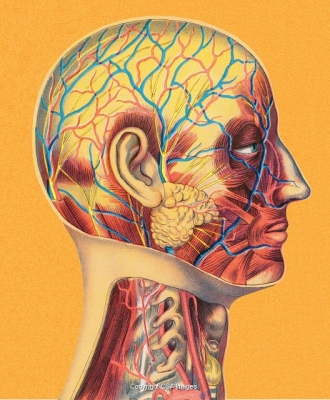
Frontal bone
The frontal bone creates the smooth curvature of the forehead and protects the frontal lobe of the brain, especially the ethmoid bone’s horizontal plate known as the cribriform plate which allows the olfactory nerve bundles to pass through its perforated surface and bring the ceiling of the nasal cavity its sense of smell. The front of the skull and the upper part of the eye sockets are formed by this bone.
Temporal artery
This blood vessel provides a blood supply to the scalp. It is also known as cranial arteritis or giant cell arteritis. Although this condition usually occurs in the temporal arteries, it can occur in almost any medium to large artery in the body.
Temporal vein
Blood is carried away from the scalp by this vessel. The superficial temporal vein descends along the auricular anterior surface, then it joins with the maxillary vein at the level of mandibular neck. It continues further as the retromandibular vein, which drains into the internal or external jugular vein.
Brain
The brain controls movement, thinking, emotions, and memory. The brain is one of the largest and most complex organs in the human body.
It is made up of more than 100 billion nerves that communicate in trillions of connections called synapses.
Eye socket (orbit)
The two hollows eye sockets surround and protect the eyeballs. The rim of the socket is made of fairly thick bones, while the floor and nasal side of the socket is paper thin in many places. A fracture is a broken bone in the eye socket involving the rim, the floor or both.
Eyeball
The eyeball is a bilateral and spherical organ, which houses the structures responsible for vision. It lies in a bony cavity within the facial skeleton – known as the bony orbit. Anatomically, the eyeball can be divided into three parts – the fibrous, vascular and inner layers. The eyes detect light and send signals to the brain, enabling us to see.
Brainstem
The brainstem (brain stem) is the distal part of the brain that is made up of the midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata. Each of the three components has its own unique structure and function. The brainstem controls automatic functions such as breathing.
Facial vein
The facial vein, also referred to as the anterior facial vein, is a paired vessel and the main vein of the face. This vein carried blood away from the face.
Nasal cavity
The nasal cavity anatomy is essential for both breathing and our sense of smell (olfaction). This hollow area is filled with smell detecting sensors.
Buccal (cheek) nerve
The buccal nerve is the only purely sensory branch of the anterior division of the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve. It is not to be confused with the buccal branch of the facial nerve This relays sensations from the cheek to the brain.
Upper jawbone (maxilla)
The upper and lower jawbones work together to enable biting. The right and left halves of the maxilla are irregularly shaped bones that fuse together in the middle of the skull, below the nose, in an area known as the intermaxillary suture.
Dental artery
This delivers blood to the mouth and gums. It begins close to the site where the maxillary artery arises as one of two branches of the external carotid artery at the top of the back of the jaw. It runs along the outside of the lower jaw. In rare cases, it may branch directly from the external carotid artery on one side of the face while presenting normally on the other side.
Facial nerve branches
These nerves enable us to make different facial expressions. A lift of an eyebrow, the wrinkling of a nose, or the slight twinge of the corner of the mouth can tell us quite a bit: if we are paying attention, we notice these small changes and interpret not only what they indicate about the people we are interacting with, but also what they indicate regarding their demeanor towards us, and the relationships forming between us.
Spinal cord
A column of nerve cells, the spinal cord carries messages from the brain to the body. The spinal cord consists of nerves that carry incoming and outgoing messages between the brain and the rest of the body. It is also the center for reflexes, such as the knee jerk reflex
Anterior jugular vein
The anterior jugular vein is a paired blood vessel that drains the anterior aspect of the neck. It emerges from the confluence of the superficial submandibular veins beneath the chin and drains into the external jugular vein. Blood from the neck is carried away by this vein.
External jugular vein
The external jugular vein is a vein of the neck that arises from the union of the posterior division of the retromandibular vein and the posterior auricular vein. This vessel drains blood from the scalp and face.
Common carotid artery
The common carotid artery is a large elastic artery, which provides the main blood supply to the head and neck region. There is one common carotid artery on either side of the body and these arteries differ in their origin. Blood is carried to the brain by this major artery.
Picture Credit : Google




