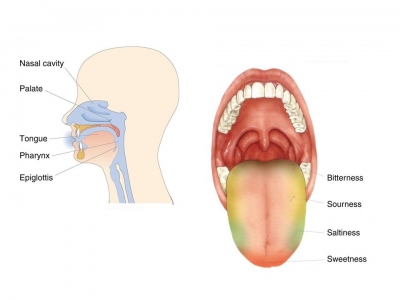
The tongue and nose act as gatekeepers to the body, sending signals to help the brain decide whether or not substances are safe to allow into the body. Millions of sensory receptors lining these areas can detect more than one trillion different smells and tastes.
Molecules in the air we breathe attach to receptors lining the sensory cells of the nasal passages, while molecules in the food we eat attach to taste receptors on the tongue. When “good” molecules are detected, the brain sends messages to the digestive system to prepare for an intake of food. More saliva is produced in the mouth, and the stomach may rumble in anticipation.
Combined senses
Smell and taste act as combined senses in the brain to create the perception of flavor. But the sense of smell is 10,000 times more sensitive than taste. To understand how much enjoyment of food comes from the smell, pinch your nose closed and eat your favourite food.
Picture Credit : Google

