We speak of nuclear reaction whenever the nucleus of an atom undergoes any change in its properties any change in properties. For example, this could be the loss of one or more protons or other particles from within the nucleus, which in turn is possibly caused by the impact of other particles. In nature this process can take place spontaneously in certain substances and gives rise to radioactivity.
Radioactivity was discovered in 1896 by the French scientist Henri Becquerel who proved that pitchblende, a mineral that contains uranium, could darken photographic plates even if they were wrapped in dark paper. It became evident to Becquerel that a very penetrating from of radiation was involved.
We now know that this radiation consists of alpha particles and that radioactive materials also give out two other types of radiation: beta and gamma. Alpha particles are not very powerful and they can be stopped by a thickness of a few sheet of paper or by a few centimeters of air. Beta rays are more penetration but can be stopped by thick cardboard, a few meters of air or thin sheet metal. Gamma rays, like X-rays, are extremely penetrating and can be very dangerous to plant and animal life. To stop them several centimeters of metal thickness is needed to reduce gamma radiation to an acceptable level.
It was not simple to produce these rays artificially and it took many years of difficult research and complicated experiments. In the end the scientists succeeded. They bombarded the atoms of certain materials with particles taken from naturally radioactive material. By increasing or decreasing this bombardment, the scientists were able to break aparkthe protective shell of electrons and reach the nucleus of an atom.
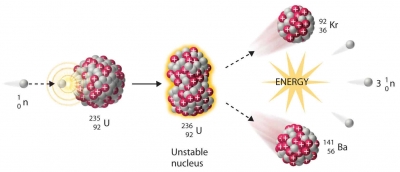
In this way nuclear fission, or the splitting of the atom, was achieved. Under such bombardment to atomic nucleus splits into two smaller nuclei. As this happens, some neutrons are rejected by the splitting atomic nucleus and collide with the nuclei of neighbouring atoms. This sets off a chain reaction, releasing enormous quantities of energy which can go out of control with disastrous results.
Nuclear reactors are complicated structures in which the chain reaction from atomic fission can be set off continued and kept under control. In this way, an atom can be split without the risk of a terrible destructive explosion. Instead, the process is done gradually and a large amount of energy is produced.
Nuclear reactors are fuelled in different ways. Nuclear fuel must always be substances which cab set off a chain reaction when bombarded with neutrons. The most commonly used elements in fueling reactors are uranium, plutonium and thorium.
At the heart of the reactor there is the moderator which is a substance that slows down the speed of the neutrons and regulates their flow. The reactor is called fast if it uses fast neutrons and thermal if the neutrons have been slowed down, thereby transferring much of their energy to the moderator.
Picture Credit : Google
