A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electron pairs between atoms. These electron pairs are known as shared pairs or bonding pairs, and the stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atoms, when they share electrons, is known as covalent bonding. For many molecules, the sharing of electrons allows each atom to attain the equivalent of a full valence shell, corresponding to a stable electronic configuration. In organic chemistry, covalent bonds are much more common than ionic bonds.
Atomic orbitals (except for s orbitals) have specific directional properties leading to different types of covalent bonds. Sigma bonds are the strongest covalent bonds and are due to head-on overlapping of orbitals on two different atoms. A single bond is usually a sigma bond. Pi bonds are weaker and are due to lateral overlap between p (or d) orbitals. A double bond between two given atoms consists of one sigma and one pi bond, and a triple bond is one sigma and two pi bonds.
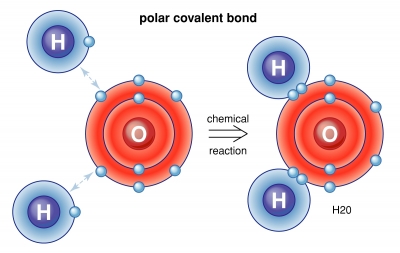
Covalent bonds are also affected by the electronegativity of the connected atoms which determines the chemical polarity of the bond. Two atoms with equal electronegativity will make nonpolar covalent bonds such as H–H. An unequal relationship creates a polar covalent bond such as with H?Cl. However polarity also requires geometric asymmetry, or else dipoles may cancel out resulting in a non-polar molecule.
Picture Credit : Google




