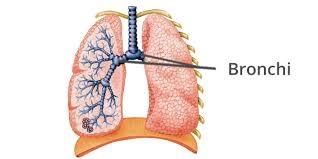
The bronchi are the airways that lead from the trachea into the lungs and then branch off into progressively smaller structures until they reach the alveoli, the tiny sacs that allow for the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the lungs.
Primary bronchi are located in the upper portion of the lungs, with secondary bronchi near the center of the lungs. Tertiary bronchi are located near the bottom of these organs, just above the bronchioles. No gas exchanges occur in any of the bronchi. When the bronchi become swollen due to irritants or infection, bronchitis results and makes breathing more difficult. Bronchitis sufferers also tend to have much more mucus and phlegm than someone without inflamed bronchi.
The secondary bronchi continue to branch off to form the tertiary bronchi, which are further divided into terminal bronchioles.
There are as many as 30,000 tiny bronchioles in each lung. They lead to the alveoli (tiny air sacs where the exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen occurs) by way of alveolar ducts.
Together, the trachea and the two primary bronchi are referred to as the bronchial tree. At the end of the bronchial tree lie the alveolar ducts, the alveolar sacs, and finally the alveoli.
The tubes that make up the bronchial tree perform the same function as the trachea. They distribute air to the lungs.
The alveoli are primarily responsible for exchanging carbon dioxide and oxygen, which occurs in the lungs.
Credit : Health Line
Picture Credit : Google



