|
Plates move at an average of between four and seven centimetres in a year. If plates collide along a deep trench beneath an ocean, one plate is pulled beneath another and melts and is recycled. On land, when continents collide, their edges are pushed up into new mountain ranges. |
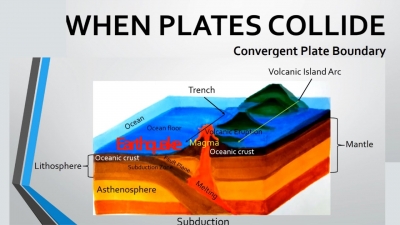
When two tectonic plates collide, they form a convergent plate boundary.
- A convergent plate boundary such as the one between the Indian Plate and the Eurasian Plate forms towering mountain ranges, like the Himalayas, as Earth’s crust is crumpled and pushed upward.
- In some cases, however, a convergent plate boundary can result in one tectonic plate diving underneath another. This process is called subduction. It involves an older, denser tectonic plate being forced deep into the planet underneath a younger, less-dense tectonic plate. When this process occurs in the ocean, a trench can be formed.
- When subduction occurs, a chain of volcanoes often develops near the convergent plate boundary.
Credit: Byju’s
Picture credit: Google




