|
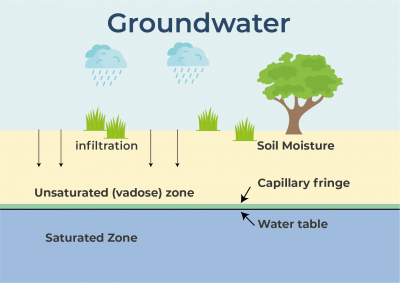
Rainwater seeps below the surface of the Earth and soaks the soil. When there is more water than the soil can absorb, it can seep even further down until it is surrounded by rocks, creating a kind of storage area, known as an aquifer. The water here is groundwater, and the upper level of water is called the water table. |
Water that has travelled down from the soil surface and collected in the spaces between sediments and the cracks within rock is called groundwater. Groundwater fills in all the empty spaces underground, in what is called the saturated zone, until it reaches an impenetrable layer of rock. Groundwater is contained and flows through bodies of rock and sediment called aquifers. The amount of time that groundwater remains in aquifers is called its residence time, which can vary widely, from a few days or weeks to 10 thousand years or more.
The top of the saturated zone is called the water table, and sitting above the water table is the unsaturated zone, where the spaces in between rocks and sediments are filled with both water and air. Water found in this zone is called soil moisture, and is distinct from groundwater.
Existing groundwater can be discharged through springs, lakes, rivers, streams, or manmade wells. It is recharged by precipitation, snowmelt, or water seepage from other sources, including irrigation and leaks from water supply systems.
Credit: National Geographic Society
Picture Credit : Google




