A climate pattern describing the unusual warming of surface waters in the easter tropical Pacific Ocean, El Nino corresponds to the warm phase of the larger phenomenon known as the El Nino-Southern Oscillation (ENSO). The pattern that describes the unusual cooling of the region’s surface waters, or the cool phase of ENSO, is referred to as La Nina. Ocean temperatures, the speed and strength of ocean currents, health of local fisheries, and the local weather of regions from Australia to South America and beyond are affected by the El Nino, which is not a regular cycle.
The El Nino phenomenon caused muddy rivers to overflow along the entire Peruvian coast in 2017.
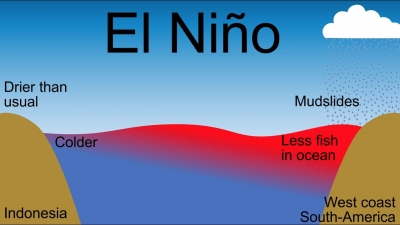
El Nino can be understood as a natural phenomenon wherein the ocean temperatures rise especially in parts of the Pacific ocean. It is the nomenclature which is referred to for a periodic development along the coast of Peru. This development is a temporary replacement of the cold current along the coast of Peru. El Nino is a Spanish word. The term El Nino basically means ‘the child’. This is due to the fact that this current starts to flow around Christmas and hence the name referring to baby Christ.
Another natural phenomenon, similar to El Nino is La Nina, which is also in news these days. The term La Nina literally means ‘ little girl’. It is termed as opposite to the phenomenon of El Nino as it results in the ‘cooling’ of the ocean water in parts of the Pacific ocean. Both of them also result in changes in atmospheric conditions along with oceanic changes.
El Nino Effects
El Nino results in the rise of sea surface temperatures
It also weakens the trade winds of the affected region
In India, Australia, it can bring about drought conditions. This affects the crop productivity largely. It has been also observed certain times, that EL Nino may not bring drought but cause heavy rainfall. In both the cases, it causes heavy damage.
However, in some other countries it may result in a complete reversal, i.e., excessive rainfall.
Mitigation Of Effects:
Keeping a check on the sea surface temperatures.
Maintaining sufficient buffer stocks of food grains and ensuring their smooth supply.
Ensuring relevant support to the farmer community including economic help.
Alternative ways to be promoted such as the practice of sustainable agriculture.
Credit : BYJUS.com
Picture Credit : Google




