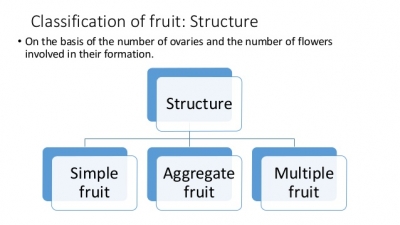
Is the tomato a fruit or vegetable?

Have you eaten an uncooked ripe tomato? Usually we consider the tomato a vegetable and use it in curries. However, it looks like a fruit in all respects. So, what is a tomato, a fruit or vegetable?
What makes a fruit different from vegetable? Vegetables do not contain seeds in them. Therefore, radish, carrot, celery and lettuce are vegetables; whereas, many vegetables, which we have never considered fruits even in the wildest of imagination, are, in fact, fruits! The tomato, therefore, is a fruit, no doubt. Along with it, beans, cucumber, squash and many more are fruits too.
However, we hardly eat them raw. Most of these ‘fruits’ are used as vegetables; and therefore, we call them vegetables out of habit.
Picture Credit : Google