Why do we feel pain?

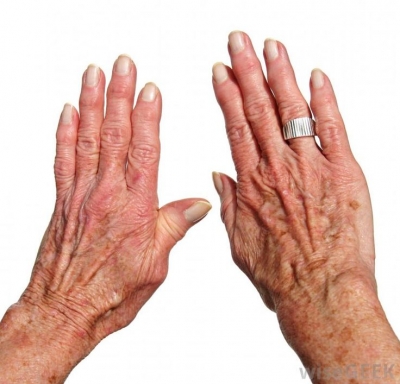
Pain is an unpleasant feeling that is usually caused by an injury, disease or other abnormality of the body. It is a warning that something is wrong somewhere in our body. Do you know why do we feel pain?
We feel pain if something burns or presses hard on the end of certain nerves which are known as pain receptors. These receptors are located throughout the body as well as in the skin. Each pain receptor is a part of a nerve which carries pain impulses to the brain.
Superficial pain is caused by receptors in the skin. A person can tell the location of the superficial pain as the skin has a large number of pain receptors. It is very difficult to pin-point the location of pain in internal regions because there are only a few pain receptors there. Sometimes deep inside the body, pain may be experienced that might get transferred to some other part of the body at some distance from the actual source of the pain. Toothache is one example of such pain.
The best treatment of pain is to treat its cause. It can be controlled by some drugs called pain killers. Aspirin is one such drug. For controlling severe pain narcotics are usually used. Long term or chronic pain is treated by interrupting the pathways of the brain or spinal cord. Opium, morphine and heroine are the important narcotics used for this purpose. These drugs cut off the paths of the nerves which carry the pain messages to the brain. The biggest disadvantage of these drugs is that they lead to addiction. In modern times, chemists have invented anaesthetic drugs and other pain killers having fewer side effects to deaden pain caused by any disease and injury.






 Cholesterol is an organic compound belonging to the steroid family and occurring either in a free state or as esters of fatty acid in practically all animal tissues. The molecular formula for cholesterol is
Cholesterol is an organic compound belonging to the steroid family and occurring either in a free state or as esters of fatty acid in practically all animal tissues. The molecular formula for cholesterol is . In a normal man it is about 0.3 percent of his average weight. It is the starting material from which the body produces bile acids, steroid hormones and pro-vitamin substances in the body. It is used by our body to help the digestive system as well.
. In a normal man it is about 0.3 percent of his average weight. It is the starting material from which the body produces bile acids, steroid hormones and pro-vitamin substances in the body. It is used by our body to help the digestive system as well.
 Dr. Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar was a world famous astrophysicist. He was awarded the Nobel Prize for physics in 1983 for his outstanding researches in the field of astronomy related to the structure and evolution of stars. He shared this prize with an American professor William Fowler. Do you know why he received this honour and what are his contributions to the astrophysics?
Dr. Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar was a world famous astrophysicist. He was awarded the Nobel Prize for physics in 1983 for his outstanding researches in the field of astronomy related to the structure and evolution of stars. He shared this prize with an American professor William Fowler. Do you know why he received this honour and what are his contributions to the astrophysics?


 Within the past hundred years there have been many advances in the design of the device called “Seismographer”. Seismographers give a record of movement and waves of the earth’s crust at their location. There is now seismic recording equipment fixed in every country — making continuous recordings. A heavy inert weight is suspended in the equipment by a spring and attached to this is a fixed pen that is in contact with paper on a rotating drum. During earthquake the instrument’s frame and the drum move, causing the pen to record a zigzag line on the paper. The pen does not move.
Within the past hundred years there have been many advances in the design of the device called “Seismographer”. Seismographers give a record of movement and waves of the earth’s crust at their location. There is now seismic recording equipment fixed in every country — making continuous recordings. A heavy inert weight is suspended in the equipment by a spring and attached to this is a fixed pen that is in contact with paper on a rotating drum. During earthquake the instrument’s frame and the drum move, causing the pen to record a zigzag line on the paper. The pen does not move. An atom is made up of three types of elementary particles called electrons, protons and neutrons. The neutrons and protons constitute the nucleus of the atom while the electrons revolve around the nucleus in different orbits. Neutron is a subatomic particle that does not have any electric charge. Protons and electrons however carry equal positive and negative charges respectively but neutron has no such charge. The mass of the neutron is slightly greater than that of the proton. Do you know who discovered the neutrons?
An atom is made up of three types of elementary particles called electrons, protons and neutrons. The neutrons and protons constitute the nucleus of the atom while the electrons revolve around the nucleus in different orbits. Neutron is a subatomic particle that does not have any electric charge. Protons and electrons however carry equal positive and negative charges respectively but neutron has no such charge. The mass of the neutron is slightly greater than that of the proton. Do you know who discovered the neutrons?