How many sweat glands are there in the human body?
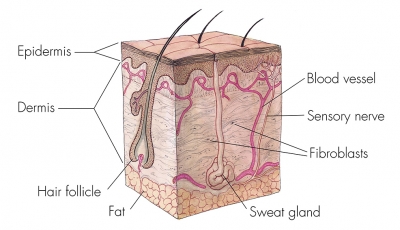
Humans have 2,000,000 to 5,000,000 eccrine sweat glands, with an average distribution of 150 to 340 per square centimetre. They are most numerous on the palms and soles and then, in decreasing order, on the head, trunk, and extremities. Some individuals have more glands than others, but there is no difference in number between men and women.
The specific function of sweat glands is to secrete water upon the surface so that it can cool the skin when it evaporates. The purpose of the glands on the palms and soles, however, is to keep these surfaces damp, to prevent flaking or hardening of the horny layer, and thus to maintain tactile sensibility. A dry hand does not grip well and is minimally sensitive.
The glands on the palms and soles develop at about 3 1/2 months of gestation, whereas those in the hairy skin are the last skin organs to take shape, appearing at five to 5 1/2 months, when all the other structures are already formed. This separation of events over time may represent a fundamental difference in the evolutionary history of the two types of glands. Those on palms and soles, which appear first and are present in all but the hooved mammals, may be more ancient; those in the hairy skin, which respond to thermal stimuli, may be more recent organs.
Picture Credit : Google













