When was actinium discovered?
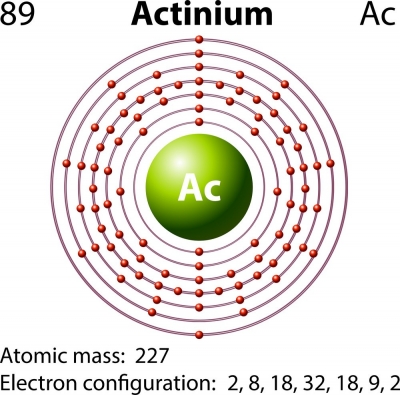
Actinium is a radioactive element. It was discovered by Andre Debierne in 1899 in Paris. He worked with Marie Curie and discovered actinium in pitchblende (a uranium ore). It was the same ore from which radium and polonium had already been extracted. He was able to identify this new element because the kind of radioactive emissions from his sample was not explainable by the presence of any known element. Although Debierne was able to discover the element, he was unable to isolate pure actinium. The high radioactivity level of actinium makes it very useful in producing neutrons.
Picture Credit : Google