What is the water cycle?
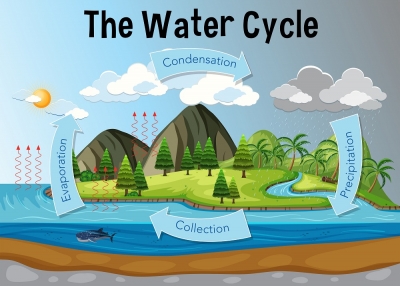
Almost three-quarters of the Earth’s surface is water. Water is found in rivers, lakes and oceans, and it can also be seen as tiny water droplets in clouds, or falling to Earth as rain or snow. Water is constantly moving from one place to another around the planet. This movement is called the water cycle.
Water on the move
The constant cycle of evaporation and condensation of water is almost entirely caused by heat from the Sun. the sun’s rays warm the land and the oceans. Heat from the Sun causes water in the ocean to evaporate, turning into invisible water vapour. Water also evaporates from rivers and lakes. As water vapour rises it cools, and condenses into tiny droplets, forming white clouds. Clouds are blown across the land by the wind. As clouds rise and cool, the tiny droplets come together and fall as rain or snow. Rain runs over the surface of the land and collects in streams and lakes. Snow from the mountains melts and forms streams. Streams join to form large rivers, which flow downhill. Rivers flow into the ocean. Groundwater eventually runs into the ocean. Water sinks into the ground, forming groundwater beneath the surface of the Earth.
Extreme conditions
Deserts are places where very little rain falls. The Atacama Desert in Chile is the driest place in the world, with only 15 mm (0.6 in) of rain every year. The wettest place on Earth is Mawsynram in India, which has 11,872 mm (467 in) of rain every year.
Picture Credit : Google