What are Rainbows?

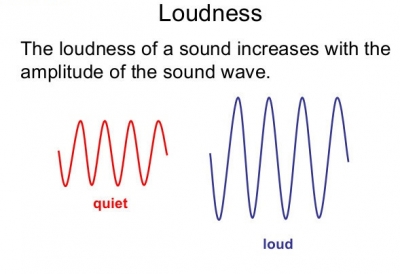
We usually see light as white, but it is actually a mixture of different colours. We know this because we can see the colours in a rainbow. When the Sun is shining low in the sky behind you and rain is falling in front of you, you may see a rainbow.
The colours of a rainbow
The colours always spread out in the same order. We call the pattern they make a spectrum. The seven main bands of colour blend into each other, creating millions of different colours.
Seeing a rainbow
As sunlight passes through a shower of raindrops, it bends and splits into different colours.
Double rainbow
If the sunlight is reflected twice inside each raindrop, you can see a see rainbow outside the main one, with its colours in the opposite order.
Colour arc
Rainbows are curved because the colours leave the raindrops at different angles.
Bright colours
Large raindrops from bright, clear rainbows, while small raindrops make faint, fading ones.
Is it the end?
If the ground wasn’t in the way, you would see the rainbow as a circle.
Inside a raindrop
Rays of sunlight shine towards the falling raindrops. When a ray enters a raindrop, it bends and the white light spreads into different colours. The light reflects off the back of the raindrop. When the light leaves the raindrop it bends again, so the colours spread out even more and shine down towards your eyes.
Picture Credit : Google