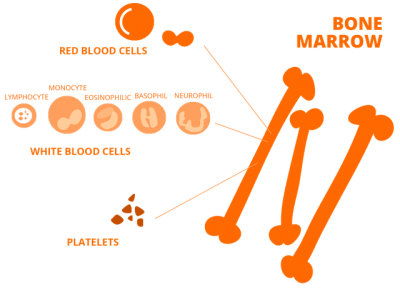
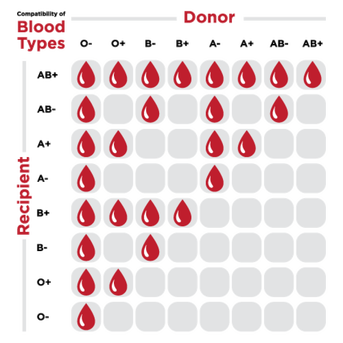
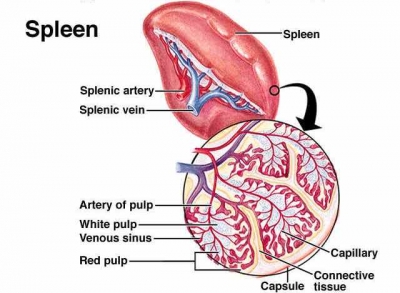
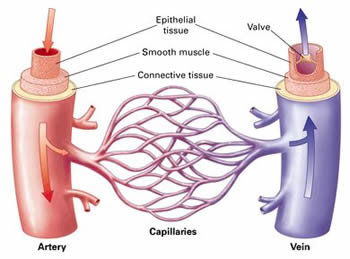
When do we learn to talk?
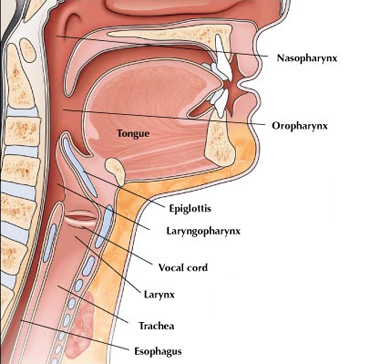
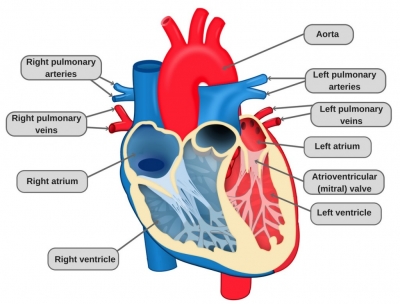
As air flows out of the lungs, we can use it to make the sounds of speech and other noises. At the top of the windpipe, in the sides of the voice box or larynx, are two stiff, shelf-like folds – called the vocal cords. Criss-crossed muscles in the voice box can pull them together so that air passes through a narrow slit between them and makes them vibrate, creating sounds. As the vocal cords are pulled tighter, they make higher-pitched sounds. As the vocal cords loosen, they make lower-pitched sounds. Of course, when we actually learn to talk, our speech depends on the development of the brain and its ability to copy the sounds that we hear.
Fact File: Although many people think of speech as our main way of communicating, we do not have to use spoken words. People who can’t speak learn a language called signing, in which hands and fingers are used to signal letters and words. |
Picture Credit : Google