HOW DO WE PERCEIVE HUMAN- LIKE ROBOTS?
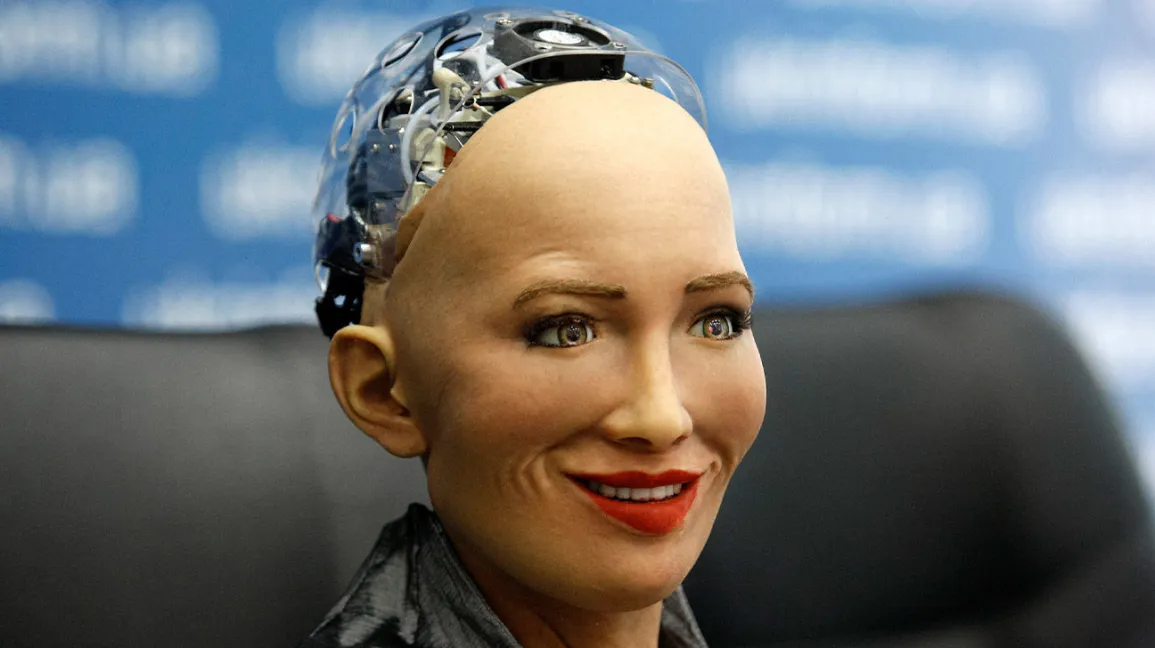

Have you ever wondered how we may perceive human-like robots? According to new research, when robots engage with people and display human-like emotions, then people may perceive them as capable of thinking and acting on their own beliefs, rather than being driven by programs.
At a time when the tendency to attribute independent thought and intentional behaviour to robots hasn't been fully understood, a group of researchers from the American Psychological Association came up with these experiments. Their results were published in the journal Technology, Mind and Behavior.
Intentional or mechanical?
Researchers examined how people perceived a human-like robot across three experiments that involved 119 participants. Participants completed a questionnaire before and after interacting with the iCub robot. Questions were typically images of the robot in different situations, asking the participants to identify if the robot's motivation in each of these situations was intentional or mechanical.
The researchers remotely controlled iCub's actions in the first two experiments. This meant that it greeted the participants, introduced itself. asked the participants for their names, and even maintained eye contact. Participants then watched three short video documentaries with the robot. which was programmed to respond with sounds and facial expressions.
The researchers programmed iCub to be more like a machine in the third experiment. This meant that it did not maintain eye contact, spoke only recorded sentences to the questionnaire before and after interacting with the iCub robot. Questions were typically images of the robot in different situations, asking the participants to identify if the robot's motivation in each of these situations was intentional or mechanical.
The researchers remotely controlled iCub's actions in the first two experiments. This meant that it greeted the participants, introduced itself. asked the participants for their names, and even maintained eye contact. Participants then watched three short video documentaries with the robot. which was programmed to respond with sounds and facial expressions.
The researchers programmed iCub to be more like a machine in the third experiment. This meant that it did not maintain eye contact, spoke only recorded sentences to the participants, and even its emotional reactions were replaced with beeps and repetitive movements of its parts.
Behaviour matters
The researchers were able to find that participants who watched videos with the human-like robot were more likely to rate the robot's actions as intentional and not programmed, while those who interacted with the machine-like robot were not. This shows that human-like behaviour is important for robots to be perceived as an intentional agent by humans.
Researchers believe that this could play a part in the design of social robots of the future. According to them, the next step of research in this area is to determine contexts where social bonding and attribution of intentionality to robots proves beneficial for the well-being of humans.
Picture Credit : Google