A gravitational singularity, spacetime singularity or simply singularity is a condition in which gravity is so intense that spacetime itself breaks down catastrophically. As such, a singularity is by definition no longer part of the regular spacetime and cannot be determined by "where" or "when". Trying to find a complete and precise definition of singularities in the theory of general relativity, the current best theory of gravity, remains a difficult problem. A singularity in general relativity can be defined by the scalar invariant curvature becoming infinite or, better, by a geodesic being incomplete.
Gravitational singularities are mainly considered in the context of general relativity, where density apparently becomes infinite at the center of a black hole, and within astrophysics and cosmology as the earliest state of the universe during the Big Bang/White Hole. Physicists are undecided whether the prediction of singularities means that they actually exist (or existed at the start of the Big Bang), or that current knowledge is insufficient to describe what happens at such extreme densities.
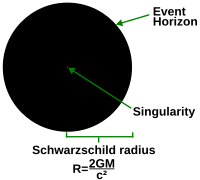
General relativity predicts that any object collapsing beyond a certain point (for stars this is the Schwarzschild radius) would form a black hole, inside which a singularity (covered by an event horizon) would be formed. The Penrose–Hawking singularity theorems define a singularity to have geodesics that cannot be extended in a smooth manner. The termination of such a geodesic is considered to be the singularity.
The initial state of the universe, at the beginning of the Big Bang, is also predicted by modern theories to have been a singularity. In this case, the universe did not collapse into a black hole, because currently-known calculations and density limits for gravitational collapse are usually based upon objects of relatively constant size, such as stars, and do not necessarily apply in the same way to rapidly expanding space such as the Big Bang. Neither general relativity nor quantum mechanics can currently describe the earliest moments of the Big Bang, but in general, quantum mechanics does not permit particles to inhabit a space smaller than their wavelengths.
Credit : Wikipedia
Picture Credit : Google

