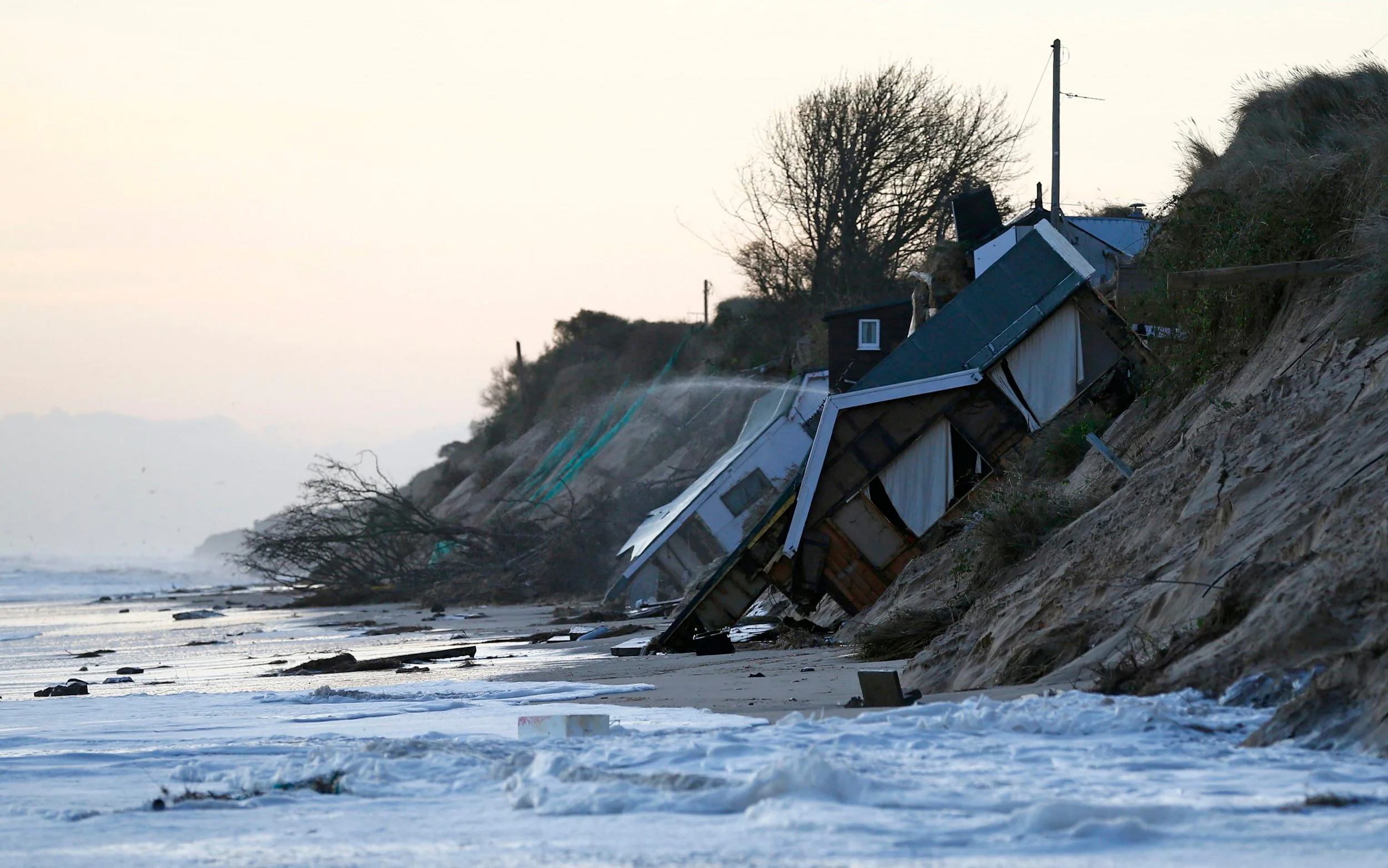
Is there anything that people can do to save the planet?
We depend on nature for everything from air, water, food and shelter to sources of energy to run our factories and businesses. So, conserving nature and preserving its biodiversity must be our priority. Here are ten simple tips to do your bit for the planet.
1. Plant trees
Trees are carbon sequesters and increasing the tree cover is perhaps one of the easiest ways to conserve nature. A tree can absorb approximately 25kg of CO2 per year. So, plant a tree to mark this day. Make it a tradition to plant a tree during prominent or celebratory occasions of your life. It can be your birthday or when you finish your academic year or any moment you feel is worth celebrating. If you do not have enough space in your home, see if you can adopt your friend's yard or make use of the space managed by your area's residents' association. Where you do it, make sure that the plant is taken care of Encourage friends and family to take up the practice as well.
2. Conserve energy
We derive our energy from nature. Everything that is manmade runs on energy obtained from nature. Quite often, a lot of energy also goes to waste. By changing a few habits you can help save energy at home. These include small actions such as turning off the lights (when not in use or when you can depend on daylight), unplugging appliances when not in use, not charging your phone overnight, turning off your faucet when you aren't using water, taking less time in the shower, reusing waste water in the kitchen gardens and so on. This will help reduce carbon footprint and in turn help in conserving nature. PHOTO: UNSPLASH IMAGES
3.3Rs
The 3Rs of "Reduce", "Reuse", "Recycle" is perhaps one of the ultimate mantras for nature conservation. These three small words will help manage waste, save the ecosystem, prevent marine animal casualties and address climate change. The first step is to reduce the waste you generate. This will ensure that less waste ends up in landfills or oceans. Effective waste segregation is the key to this. This helps recover materials for recycling and composting. Reuse articles that you can. And lastly, recycle. This helps prevent soil and water pollution. PHOTO: UNSPLASH IMAGES
4. Use public transport
One of the major polluters is the global transport sector. It is responsible for approximately one-quarter of greenhouse gas emissions, according to experts. And 95% of the world's transport energy is still obtained from fossil fuels. Personal transportation adds to the probelm, adding to the greenhouse emissions. The easiest way to avoid this is by switching to public transport. If this is not a practical solution every time, you can still choose public transport twice or thrice a week or during specific hours. This, when done on a regular basis, can significantly help reduce carbon emissions. Alternately, switching to green modes of travel such as a bicycle can help prevent your carbon footprint.
5. Stop using single-use plastics and disposables
Single-use plastics and disposable cups and utensils have infiltrated our day-to-day life and upended it. Those disposable grocery bags and disposable utensils you use eventually ends up on the earth, polluting our soil. oceans, and marine life. These disposables can easily be replaced with environmentally responsible counterparts. Make a commitment to take out at least one disposable article from your lifestyle. Perhaps. carry a cloth bag to the supermarket instead of asking them for a plastic one. Maybe switch out your lunch box for one made of metal. This can be a good start. And slowly you can make a lifestyle switch by eschewing other disposables. PHOTO: UNSPLASH IMAGES
6. Eat less meat
It is estimated that 80% of forest loss is caused by the conversion of forest land to agricultural land. It leads to habitat destruction and loss of our green cover. Eating less meat can help prevent this and preserve biodiversity and the ecosystem. Since we all have our food preferences, it may not be easy to switch to vegetarianism or veganism. But you can be more aware and mindful of the food on your plate and choose to eat less meat. For instance. you can limit meat consumption to one or two days a week or reduce the number of meals with meat. PHOTO: UNSPLASH IMAGES
7. Use windows and not AC
Our world is heating up and the surging heat has made us all dependent on air conditioning, the demand for which is increasing by the day. Did you know that air conditioners are also a contributor to the climate crisis? They consume more electricity than any other appliance in your home and consume about 10% of global electricity (along with electric fans). So next time, when possible, open the windows and let the cool breeze in.
8. Explore thrifting
Fast fashion is one of the greatest threats to the environment. Did you know that it takes about 2,700 litres of water to make just one t-shirt. Or that a pair of jeans requires 7,600 litres of water? With a consumer base that updates its wardrobe according to trends in the fashion industry, the damage to the planet has been exponential. This trend depletes natural resources and harms the planet. This is where thrift shopping comes in. Anyone who has had an older sibling would be no stranger to using their toys, books, or school paraphernalia, thus giving the article a fresh lease of life. This is the concept of thrift shopping. It means using hand-me-downs or second-hand articles. It applies to all forms of merchandise such as clothes, games, toys, shoes, books, appliances, furniture, and so on. It's time to break the cycle of single-use apparel or appliances and shop at thrift stores. Also, remember to let your friends and family know you are using a thrifted article and the positive impact your move has on nature's conservation.
9. Embrace minimalism
Minimalism is a lifestyle choice where you make mindful, deliberate choices of buying only what you truly need. As such you make do with less and avoid overconsumption, which is one of the major contributors to the exploitation and depletion of natural resources. By consuming only what's essential for your living, your ecological footprint gets reduced. Thereby, the individual environmental impact is limited. Replace consumerism with eco-minimalism. PHOTO: UNSPLASH IMAGES
10. Spend time volunteering
One way to help conserve nature is to help organisations that are working in the field directly. You can do this by volunteering your time and services at non-profit environmental organisations. These organisations run on donations and they are always on the lookout for people who can help them. Here you may get to actively participate in the community and work on projects aimed at conserving nature and get on-field experience.
Picture Credit: Google